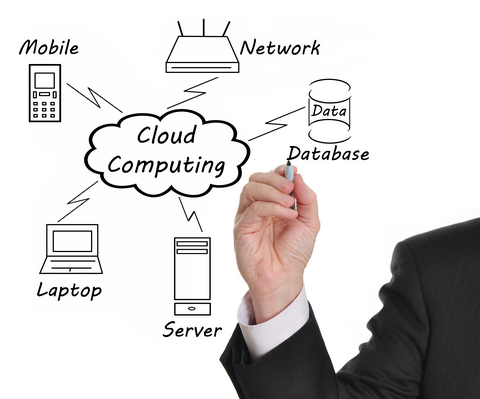
Gear up with the Season’s Latest Trend- Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, in simple words, is like an allegory for the internet. It is a subscription-based service where one can obtain networked storage space and computer resources that include all the components of a network.
For better understanding, one could think of cloud computing when chatting over the internet. Consider Google chat or Skype, for instance. These applications house the hardware and software essentials in their data centers to create and use a personal chat account. When one wants to access chat, appropriate web browser is opened and the user is asked to sign in. The key part of the process is to have internet access. Chat is never housed on physical computer; it is accessed over an internet connection, and can be accessed from any corner of the world as long as one has access to the internet. Cloud computing also works along these lines. One can access any information stored in the server as long as one can connect to the internet. One can pull out five year old business reports, alter it, use it and even build on it. This, of course, needs security clearance. Even though cloud allows mobility, one needs to follow the specified security protocols.
Conventionally, computers which acted as data storage devices would usually be grounded in one room. Access to information while on the move would be a task like no other. The cloud, fortunately, doesn’t entail such drawbacks. The cloud eliminates the need to be in the same locality as the hardware which stores data. A cloud provider can own as well as house the hardware plus the software necessary to run both, home or business applications. The cloud enables its users to access information from anywhere at any given time. Cloud computing entrusts services which is essentially centralized with that of a user’s data, software and computation on a published application programming interface (API) over a network.
There are different types of clouds that one can subscribe to depending on the requirement. As a home user or small business owner, most people are likely to use public cloud services.
- Public Cloud – A public cloud can be accessed by any subscriber who has an internet connection and an access to the cloud space.
- Private Cloud – A private cloud is accessible to just a specific group or organization and restricts access to everyone else.
- Community Cloud – A community cloud is pooled among two or more organizations which have similar cloud requests.
- Hybrid Cloud – A hybrid cloud is fundamentally an amalgamation of at least two clouds where the clouds included are a mix of public or private organization, or a community.
The sole purpose of having cloud computing boils down to saving a lot of effort and money one would spend on while installing and maintaining compound hardware and applications. Cloud provides the same services on a pay-as- you-go basis. Businesses do not always generate their own resources– utilities are bought when required. The same holds good for the essential IT services that can be managed better on the exterior.
Users can access cloud computing through networked client devices, such as desktops, laptops, tablets or even smart phones. Most cloud clients depend on cloud computing for all the frequent use of their applications. Most cloud applications do not need explicit software and instead need a web browser to access the cloud application. Some of the bequest applications are delivered through a screen-sharing technology. Today, for the major part, IT has to plug into cloud-based services individually, but cloud computing aggregators and integrators are already up-and-coming.
In the present day, there are scores of vendors that offer cloud services. The services offered by these vendors depend upon the facilities as well as the pricing models provided by them. Some of the earliest vendors included Amazon which offered sophisticated services followed by Google and Microsoft.
To sum up, the cloud provides numerous options for the everyday computer user as well as to the large and small businesses. It provides a wide variety of computing and enhances the usability by providing access through any internet connection. However, this increased ease also comes with a flipside. The users have less control over who can access the data and where it is stored. Users also must be aware of the security risks of having data stored over cloud because anyone could access the cloud through unsecured connections. The best way to keep it safe is by understanding the terms and conditions of the cloud provider and the system itself.
Data Center Talk updates its resources everyday. Visit us to know of the latest technology and standards from the data center world.
Please leave your views and comments on DCT Forum.